
![]()

HOME
ON
THE WAY TO HARMONY
REACHING
A STATE OF HARMONY
COACHING
THE WAY-YANNIS
FITNESS TOOLS ONLINE
A SAFE PATH TO THE STATE
THE FITNESS STATE FLEXIBILITY
THE FITNESS STATE NUTRITION THE
FITNESS STATE TREATMENT
ANATOMY
FITNESS MYTHS VS FACTS
TESTIMONIALS
DOWNLOAD
| A
SAFE PATH TO THE STATE OPTIMUM PERFORMANCE TRAINING MODEL |
 |
TRAIN.
PHASE |
SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE | TRAINING FOCUS | CONCEPT DEFINITIONS |
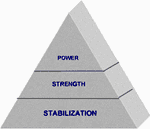
| INTEGRATED TRAINING OVERALL | The Optimum Performance Training model
is divided into three different stages. These include the Stabilization,
Strength and Power. Each stage is built upon and dependent on the
prior stage. Within each stage there exists specific phases of training
that progress a client through the stage. |
The goal of an Integrated functional training program is to prevent injury, decrease body fat, and increase lean muscle mass, strength, endurance, flexibility and performance in some specific activity. All integrated, functional training programs must be multi-planar, multi-joint, multi-dimensional, proprioceptively enriched and activity specific. | Integrated training is a comprehensive
training approach that strives to improve all components (flexibility,
balance, endurance, strength, and power), necessary to allow a client
to achieve optimum performance. Function is integrated, multi-planar movement that involves acceleration, deceleration, and stabilization. |
| STABILIZATION PHASE | -You are only as strong as Your weakest link.-Prime mover muscles can only be recruited to the degree that the joint is stable. | The main focus of the Stabilization stage is to increase stabilization strength and develop optimal neuromuscular efficiency. | The kinetic chain is made up of the soft
tissue system (muscle, ligament, tendon, and fascia), neural system,
and articular system. Each of these systems works interdependently
to allow structural and functional efficiency. If any of the systems
do not work efficiently, compensations and adaptations occur in the
other systems. These compensations and adaptations lead to tissue
overload, decreased performance, and predictable patterns of injury. Stabilization strength is the ability of the stabilizing muscles to provide dynamic joint stabilization and postural equilibrium during functional activities. |
| STRENTH PHASE | -Most Injuries happen on the transverse plane and during deceleration.-Strength training improves the transition from concentric to isometric to eccentric phase and vise versa.-It increases the intra-muscular as well as the inter-muscular coordination of the neuromuscular system.-Maximal strength and power combined enhance the overall performance ability. | The Strength Stage of training follows the successful completion of the Stabilization Stage. In this stage of the Optimum Performance Training model, higher levels of balance and core stabilization are warranted.The emphasis in the Strength Stage is on dynamic joint stabilization, stabilization endurance and improving intra-muscular and inter-muscular coordination. | Neuromuscular efficiency is the ability
of the neuromuscular system to allow agonists, antagonists, stabilizers
and neutralizers to work synergistically to produce force (concentric),
reduce force (eccentric) and dynamically stabilize (isometric) the
entire kinetic chain in all three planes of motion. Dynamic joint stabilization is the ability of the stabilizing muscles of a joint to produce optimum stabilization during functional, multi-planar movements. |
| POWERPHASE | -Combination of Strength and Power.-Increase of speed strength-Sport Specific Training mimics the specific sport moves.-Development of acceleration ability. | The Power Stage of the Optimum Performance Training model should only be entered upon successful completion of the two previous stages. This stage of training emphasizes the development of speed and power. The speed and power with which people can produce muscular actions determine successful performance in many sports as well as everyday activities. This stage of training is necessary to enhance the speed spectrum that the body is allowed to operate within. The speed with which muscles are able to exert force is dictated by the neuromuscular system. Therefore, the body will only be able to move within a set range of speed that is determined by the nervous system. | Stabilization endurance is the ability of the stabilization mechanisms of the kinetic chain to sustain proper levels of stabilization to allow for prolonged neuromuscular efficiency.Intra-muscular coordination is the ability of the neuromuscular system to allow optimal levels of motor unit recruitment and synchronization within a muscle.Inter-muscular coordination is the ability of the neuromuscular system to allow all muscles to work together with proper activation and timing between them. |
Notes
taken from: “The Essentials of Integrated Training” Series
by Mike Clark-National Academy of Sports Medicine.
* Optimum Performance Training is a Trademark of NASM.
To Contact NASM:
26632 Agoura Road
Calabasas, CA 91302
Call 800-460-NASM (6276) toll free
or 818-878-9203
Fax: 818-878-9288